The Privacy Battle Between Two Giants – Explained Without Bias
🧠 Introduction — Telegram vs WhatsApp: A Quiet War Over Your Conversations
You don’t think about it when you send a message.
A joke. A file. A location. A secret.
It takes a second. It disappears from your screen. But where does it really go? Who holds it? Who could read it?
In 2025, the real battle for your privacy isn’t happening in courtrooms or parliaments — it’s unfolding inside the apps you trust most. Two names top that list: Telegram and WhatsApp. They sit on your phone like equals. But under the surface, they couldn’t be more different.
This isn’t a comparison of features. It’s a forensic look at trust.
At who builds the app. Who owns your data. Who knocks when governments come calling. And who opens the door.
This article won’t tell you what to use — but by the end, you’ll know what you’re really choosing.
Let’s dive beneath the logos and marketing — and examine the true privacy posture of both messengers.
⚠️ Disclaimer
This article is intended for educational and informational purposes only. It does not promote or criticize any specific platform, nor does it offer legal or cybersecurity advice. All evaluations are based on publicly available information and technical documentation as of July 2025. Readers are encouraged to conduct their own research and exercise caution when choosing messaging apps for sensitive communication.
Telegram vs WhatsApp: Global Usage in the 20 Most Populous Countries (2025)
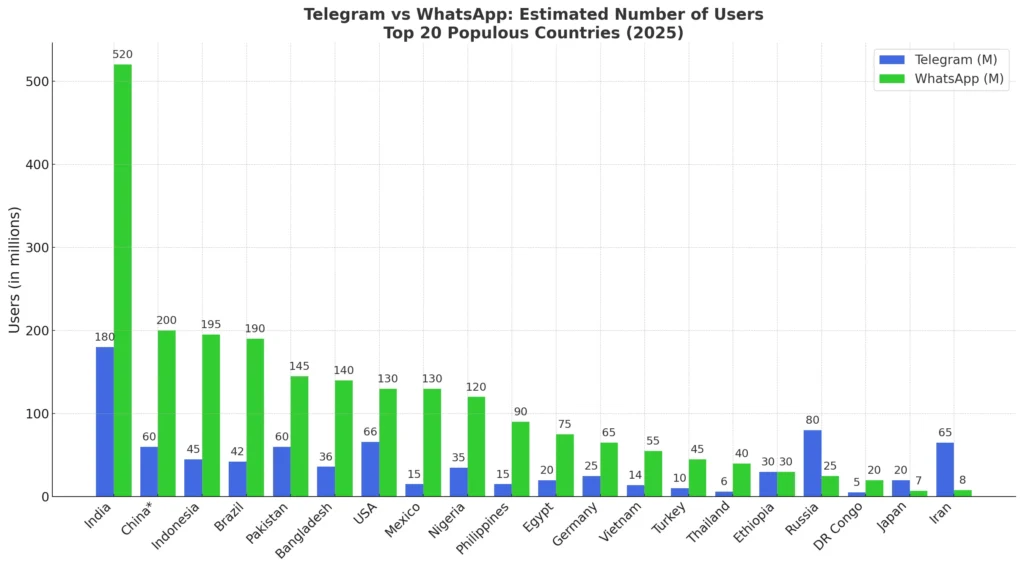
📊 Global Active Users (As of July 2025)
| Platform | Active Users 🌍 | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| ~2.6–2.7 billion | The global leader. Especially dominant in India, Brazil, Indonesia, and Nigeria. | |
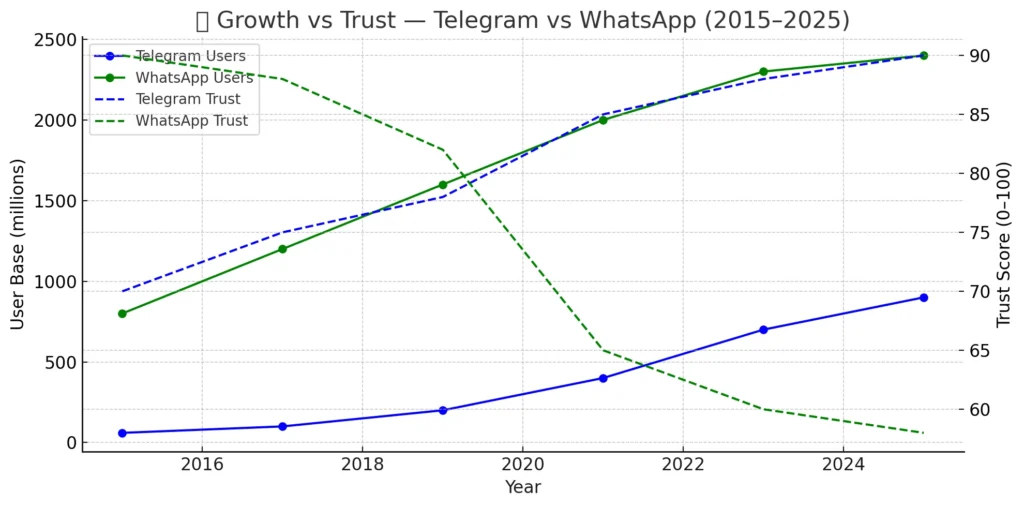
| Telegram | ~900 million – 1 billion | Rapid growth since 2021, fueled by backlash against WhatsApp’s data policy changes and increasing censorship resistance. |
📈 Telegram: Growth Trajectory
| Date | Estimated Users |
|---|---|
| January 2021 | ~500 million |
| January 2022 | ~600 million |
| January 2023 | ~700 million |
| January 2024 | ~850 million |
| July 2025 | ~900 million – 1 billion (varies by source) |
Telegram has been growing by approximately 100–150 million users per year, largely due to:
- Protest movements and digital migration
- Adoption in censorship-heavy countries
- Reputation losses at WhatsApp fueling user shifts
📈 WhatsApp: Plateauing Growth
| Date | Estimated Users |
|---|---|
| January 2020 | ~2.0 billion |
| January 2023 | ~2.4 billion |
| July 2025 | ~2.6–2.7 billion |
Growth has slowed in recent years, particularly in Europe and the United States. However, WhatsApp remains dominant in key global regions:
- 🇮🇳 India: Over 600 million users
- 🇧🇷 Brazil: ~140 million
- 🇮🇩 Indonesia, 🇲🇽 Mexico, 🇳🇬 Nigeria — major strongholds
🧠 Notes
- Telegram’s numbers are approximate, as the company does not publish quarterly user reports.
- WhatsApp data is more precise, since Meta reports regularly to investors.
🔧 1. The Battle of Architectures: Cloud vs Device
At their core, Telegram and WhatsApp rely on fundamentally different security models.
| Feature | Telegram | |
|---|---|---|
| Encryption Type | Client-server (default) | End-to-end (default) |
| Secret Chats | End-to-end (manual) | All chats encrypted E2E |
| Message Storage | Cloud-based (Telegram servers) | Device-to-device only |
| Backup Encryption | Optional via 2FA (Telegram) | Encrypted backups (since 2021) |
| Code Transparency | Partially open source | Not open source (only Signal base) |
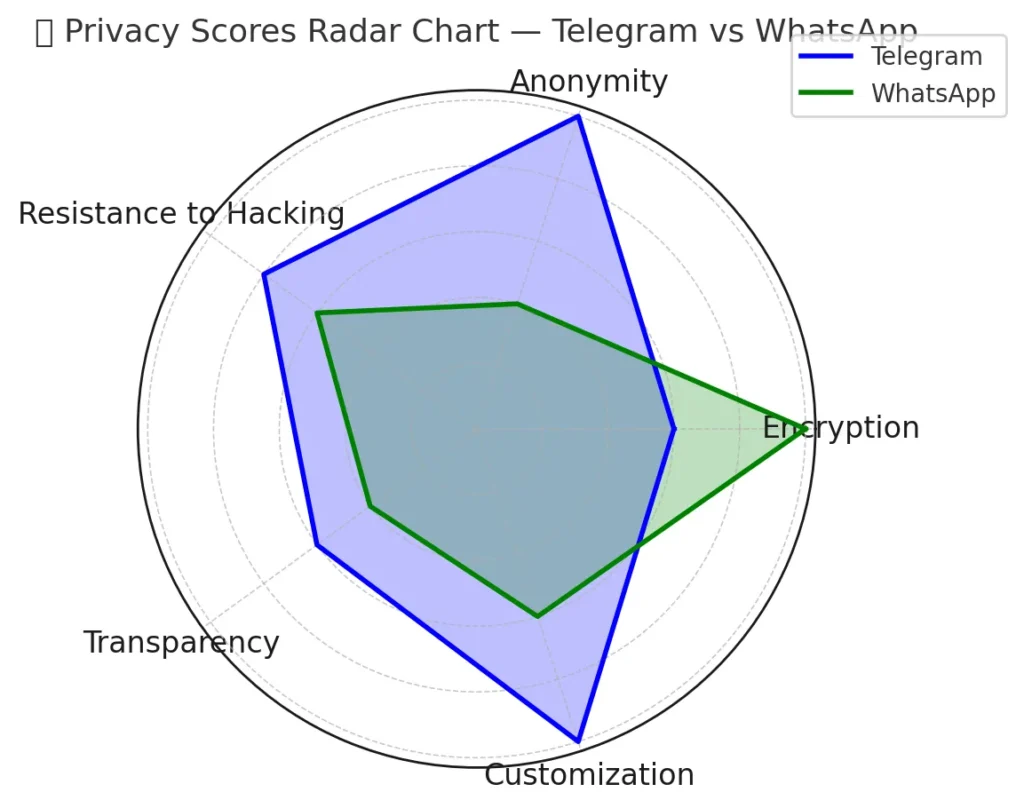
🕵️ Privacy scores radar:
🛠 WhatsApp: End-to-End by Default
WhatsApp uses the Signal Protocol for end-to-end encryption (E2EE).
That means messages are encrypted on your phone and only decrypted on the recipient’s. Not even WhatsApp can read them.
Group chats? Encrypted.
Calls? Encrypted.
Media? Encrypted.
But the devil is in the metadata — we’ll get to that soon.
☁️ Telegram: The Cloud is the Message
Telegram, in contrast, does not encrypt chats end-to-end by default.
Instead, it uses client-server encryption: your messages are encrypted between you and Telegram’s cloud — and decrypted again for the recipient.
This enables features like multi-device sync and chat history stored in the cloud.
Want full end-to-end protection? You’ll need to manually switch to “Secret Chat” mode, which disables syncing, bots, stickers, and some media types.
Telegram argues this trade-off gives users flexibility.
But for purists and privacy hawks, default E2EE is non-negotiable.
🕵️ 2. Privacy Promises vs Real-World Practices
Both apps say they care about privacy.
But one is owned by Meta. The other by an elusive billionaire.
Let’s see who’s more trustworthy.
📄 Meta (WhatsApp): A Mixed Record
Meta (Facebook’s parent company) has a long history of data mishandling, from the Cambridge Analytica scandal to political ad targeting.
While WhatsApp uses solid encryption, it’s not open-source, and metadata collection remains aggressive.
In 2021, WhatsApp updated its privacy policy to share more data with Facebook, triggering backlash and a wave of users migrating to Telegram and Signal.
💬 Telegram: Controlled by Durov, Not a Corporation
Telegram is run by Pavel Durov, a Russian-born entrepreneur who defied the Kremlin and built Telegram as an “independent” platform.
He claims to have refused backdoors, state cooperation, and surveillance demands — even moving servers to different jurisdictions.
But Telegram is also opaque:
- No external audit of its encryption.
- Part of the app remains closed-source.
- “Trust us, we’re good guys” is the default PR line.
While not owned by a corporate giant, Telegram’s model depends on trust in Durov’s vision — and his funding.
🔓 3. Security Breaches and Past Attacks
When it comes to privacy, history matters. No app is immune to security flaws — but how a company reacts to incidents reveals its real values.
📉 WhatsApp: A Magnet for State-Level Exploits
WhatsApp has been the target of multiple high-profile zero-day attacks, often involving state actors and surveillance firms:
- 2019 – Pegasus Exploit: NSO Group used a vulnerability in WhatsApp’s call function to install spyware on phones — even without the user answering the call.
- Victims: Journalists, lawyers, human rights activists.
- Fallout: WhatsApp patched the flaw, sued NSO Group, and notified 1,400 users.
Another example: in 2021, a security researcher discovered a double-free vulnerability that allowed remote code execution via a specially crafted video file.
While WhatsApp has a solid engineering team and rolls out patches quickly, its large attack surface and integration with Meta’s ecosystem make it a high-value target.
🔍 Telegram: Fewer Exploits, But More Obscurity
Telegram hasn’t seen the same scale of public breaches, but that doesn’t mean it’s bulletproof:
- Telegram developed its own encryption protocol (MTProto) — which has been criticized for lacking peer review and relying on custom cryptography.
- In 2017, the Iranian government exploited Telegram’s SMS authentication system to access accounts — a flaw in process, not protocol.
- In 2022, German researchers identified potential risks in Telegram’s group management logic, including replay attacks and impersonation vulnerabilities in channels.
Telegram often touts a “clean record,” but critics argue this is due to its opacity, not superiority. It doesn’t publish detailed CVEs (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures), and no independent audit has been completed for MTProto.
In short:
- WhatsApp gets hacked more — but is more transparent.
- Telegram appears safer — but hides more.
📡 4. Metadata & Data Collection — Who Knows What You’re Doing?
Even if your messages are encrypted, your metadata often isn’t. And that metadata — who you talk to, when, for how long — can be as revealing as the content itself.
🧾 WhatsApp: Encryption, But Not Anonymity
Despite using end-to-end encryption for all chats, WhatsApp collects and retains extensive metadata, including:
- Phone numbers of both parties
- Device info and location data (via IP)
- Message timestamps
- Group membership
- Contact list hashes (unless manually disabled)
Meta claims it doesn’t read your messages — but it doesn’t need to. With access to such detailed behavioral data, profiling becomes trivially easy.
💥 In 2021, ProPublica revealed that WhatsApp employs thousands of content moderators who review messages when they’re reported — effectively bypassing E2EE via user-side screenshots and reports.
Meta also uses this metadata to:
- Feed ad targeting (outside WhatsApp, in Facebook & Instagram)
- Cooperate with law enforcement via data requests (even without reading your messages)
🔐 Telegram: Minimal Metadata, but With a Catch
Telegram claims to store very little metadata, especially in Secret Chats:
- No access to message content
- No phone call records
- No cloud backup for Secret Chats
However, for default (non-secret) chats, Telegram stores message content on its own servers. These messages are encrypted at rest but accessible by Telegram itself — under specific legal conditions.
Telegram’s 2023 privacy policy states:
“To comply with applicable laws, we may store IP addresses and metadata for up to 12 months in limited cases.”
That “limited” is open to interpretation.
Another concern: Telegram accounts are tied to phone numbers, making anonymous use tricky. Though username-only contact is possible, the platform doesn’t yet support full anonymous registration (e.g., via decentralized ID or email-only).
🧠 Summary of Sections 3 & 4:
| 🔍 Aspect | Telegram | |
|---|---|---|
| Known Security Breaches | Fewer, less transparent | Multiple, including Pegasus attack |
| Encryption Protocol | MTProto (custom, partly audited) | Signal Protocol (open, widely vetted) |
| Metadata Collection | Minimal (esp. in Secret Chats) | Extensive, including device/location |
| Access to Message Content | Possible in non-secret chats | Impossible due to full E2EE |
| Data Sharing with Parent | No parent company | Shared with Meta ecosystem |
🧩 5. User Control, Open Source, and Transparency
In privacy, what you control is what you own. Let’s look at what Telegram and WhatsApp actually allow you — and the world — to verify.
🔓 Open Source or Closed Club?
🧪 WhatsApp:
- Core encryption (Signal Protocol) is open source and widely vetted.
- But the app itself is closed-source — users cannot verify what the code actually sends or stores.
- Updates go through Meta’s infrastructure, and the final build is unverifiable by the public.
This means: while the math is solid, the app is a black box. You must trust Meta to implement it properly — and not sneak in telemetry or backdoors.
🔍 Telegram:
- Telegram’s mobile apps are open source (on GitHub), and anyone can audit the code.
- But the server-side code is fully closed-source.
- Encryption protocol (MTProto) is Telegram’s own invention — and although partially documented, it lacks wide academic scrutiny.
The result is ironic: Telegram appears more open, but only on the surface. WhatsApp uses a battle-tested encryption model — but hides its inner workings.
🎛️ User Controls & Features
| Control Feature | Telegram | |
|---|---|---|
| Multi-device support | ✅ Yes (via cloud sync) | 🔸 Yes (limited via QR login) |
| Username (no phone shown) | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
| Self-destructing messages | ✅ Yes (per chat, even in defaults) | ✅ Yes (timers added in 2021) |
| Export chat history | ✅ JSON, HTML, text | 🔸 Only for backups |
| Advanced privacy settings | ✅ Hide phone, last seen, groups | ✅ Blocked contacts, last seen, status |
| Backup control | ✅ Full (you choose) | 🔸 Backups to iCloud/Google (optional) |
Telegram excels at user-level privacy control — you can use it without revealing your phone number, fine-tune visibility, and download all your data at will.
WhatsApp is catching up, but remains tightly tethered to your phone and identity. It’s not anonymous — by design.
🚫 6. Censorship Resistance and Government Pressure
If privacy is freedom from corporations, then censorship resistance is freedom from governments.
Here, the ideological divide between WhatsApp and Telegram is stark.
🏛️ WhatsApp: Lawful Compliance
As part of Meta, WhatsApp complies with legal requests from dozens of governments, including the U.S., India, Brazil, and EU nations.
- In 2020–2024, WhatsApp responded to tens of thousands of government data requests.
- Though it cannot decrypt messages, it often provides:
- Account metadata
- Timestamps
- IP addresses
- Contact list hashes (if backed up)
- WhatsApp has also been criticized for removing content or banning accounts in response to pressure from India and Brazil.
In one instance (2023), WhatsApp blocked several opposition figures in India during an election dispute — citing “compliance with local laws.”
In short: WhatsApp protects message content, but not the right to access or speak freely.
🌐 Telegram: Banned, Chased, and Still Running
Telegram has been banned or blocked in multiple countries:
- Iran
- China
- Pakistan
- Russia (2018–2020)
- Belarus (periodically)
Why? Because Telegram:
- Refused to hand over encryption keys
- Ignored censorship requests
- Allowed opposition movements to organize
Pavel Durov publicly declared:
“We will never compromise our users’ privacy for the sake of political gain.”
To counter censorship, Telegram implements:
- Proxy server support (MTProxy)
- Decentralized CDN nodes (for content delivery)
- Domain fronting in some versions
However, critics note that Telegram has quietly complied in some regions by limiting certain features — like large channels or specific content visibility in local app stores.
🛡️ Hardening Tips: How to Stay Safe on Telegram & WhatsApp
| Telegram | |
|---|---|
| ✅ Use Secret Chats for end-to-end encryption | ✅ Turn on Encrypted Backups in settings |
| 🚫 Disable Contact Sync (no address book upload) | ⚙️ Revoke Metadata Permissions (location, usage) |
| 🧑💻 Use Usernames instead of phone numbers | ☁️ Avoid backups to Google Drive / iCloud |
| 🔐 Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) for login | 🔒 Use Screen Lock + 2FA (PIN/email) |
| 👁️ Be cautious with public channels & bots | 🧩 Don’t click unknown links or group invites |
📘 Pro Tip:
Even the most secure app is only as strong as your settings. Harden your messenger like you harden your password.
🧠 Summary of Sections 5 & 6:
| Category | Telegram | |
|---|---|---|
| App Code Transparency | Partially open (clients only) | Closed-source (except encryption protocol) |
| Server Code Transparency | ❌ Closed | ❌ Closed |
| Encryption Protocol Review | Limited academic scrutiny (MTProto) | Openly vetted (Signal Protocol) |
| Phone Number Privacy | ✅ Can hide / use username | ❌ Phone required & visible |
| Censorship Resistance | ✅ High (proxies, anti-censorship tools) | 🔸 Low (compliance with state requests) |
| Government Compliance | ❌ Often refuses | ✅ Responds to legal requests globally |
🌐 7. Messaging Under Fire: Where Telegram or WhatsApp Are Blocked
Privacy doesn’t exist in a vacuum. In some countries, messaging apps aren’t just monitored — they’re outright banned.
This section maps out where Telegram and WhatsApp face censorship, legal restrictions, or direct blocking by governments.
🚫 Telegram: Targeted for Its Defiance
Telegram has been blocked or restricted in several countries — often because it refused to cooperate with government demands for surveillance or censorship.
| Country | Status | Reason for Block |
|---|---|---|
| China | ❌ Fully blocked (since 2015) | Used by activists; refused cooperation |
| Iran | ❌ Blocked since 2018 | Protest coordination; refusal to store data in Iran |
| Pakistan | ⚠️ Intermittent blocking | Religious content, protest channels |
| Russia | ❌ Blocked 2018–2020 | Refused to hand over encryption keys |
| Belarus | ⚠️ Temporarily restricted | Used during anti-government protests |
| India | ✅ Available, but under scrutiny | Investigations into extremist content, regional website blocks in 2019 |
| Egypt | ⚠️ Short-term blocking in 2020 | Alleged national security risks |
| Venezuela | ⚠️ Throttled during protests | Suppression of opposition channels |
| Vietnam | ⚠️ Throttled or slowed | Government pressure on content visibility |
🔍 In most of these cases, Telegram was targeted not because of technical flaws, but because of its resistance to surveillance and its popularity among opposition groups.
Durov’s public stance:
“We will never cooperate with censorship regimes.”
However, in some regions, Telegram has quietly disabled features (e.g., channel visibility in local app stores) to avoid full bans.
🚫 WhatsApp: The Metadata Gatekeeper Under Pressure
Unlike Telegram, WhatsApp usually complies with legal data requests. But this hasn’t saved it from being blocked in a few countries — usually for different reasons.
| Country | Status | Reason for Restriction |
|---|---|---|
| China | ❌ Blocked since 2017 | Encrypted calls and text bypass censorship |
| Iran | ⚠️ Limited functionality | Preferred domestic apps (e.g., Soroush) |
| Qatar & UAE | ⚠️ Voice/video calls blocked | Telecom regulation & national telco interests |
| Brazil | ⚠️ Temporarily blocked (2015–2016) | Court orders over refusal to hand over metadata |
| India | ✅ Available | But faces frequent government takedown requests |
| Cuba | ⚠️ Slowed or restricted | Bandwidth prioritization policies |
Unlike Telegram, WhatsApp is rarely fully blocked — but it’s often throttled, pressured, or surveilled.
🧭 Why This Matters
- Telegram gets banned for refusing to share data.
- WhatsApp gets pressured because it holds metadata.
So if you’re in a country with authoritarian tendencies, neither app is immune — and your choice may depend on local dynamics and the threat model.
Always use a secure VPN or proxy (like MTProxy) in censorship-heavy regions — and assume that even encrypted apps can be politically targeted.
📘 8 UX/UI Feature Breakdown and Commentary:
🔷 Telegram UX/UI Highlights:
Minimalist Design with Modular Controls: Telegram’s interface is clean and modern, offering modular settings with deep customization. Users can personalize themes, chat backgrounds, and interface animations.
Privacy Visibility: The “Secret Chat” option is a clear, visible toggle — giving advanced users direct control over encryption settings. However, for non-technical users, this may cause confusion as it’s not the default mode.
Username-Based Messaging: Users can chat via @usernames instead of phone numbers — a major plus for privacy and anonymity.
Built-in Tools: Telegram integrates polls, quizzes, scheduled messages, and silent sends right into the chat UI — enhancing functionality without clutter.
Powerful Search and Media Management: Rich file previews, categorized media sections, and granular search tools make it easy to navigate large chats.
🟢 WhatsApp UX/UI Highlights:
Simplicity-First Layout: WhatsApp uses a minimalist, frictionless interface that requires almost no learning curve. Everything is familiar, linear, and optimized for casual users.
Passive Privacy: End-to-end encryption banners appear automatically in each chat. No configuration needed — a reassurance-first design choice that builds trust without effort.
Contact-Based UI: Chats are based on phone numbers. This makes setup seamless but limits anonymity. Contacts sync is deeply integrated into the UI.
Feature Integration: Voice and video calling, file sharing, and status updates are smoothly built into the navigation — making the app an all-in-one hub.
Backup Awareness: WhatsApp now shows clearer backup controls with tooltips explaining encryption status when uploading to cloud services (Google Drive / iCloud).
💡 Conclusion:
Telegram wins on customization, anonymity, and advanced control, but demands more technical awareness from the user.
WhatsApp wins on default security and frictionless UX, offering comfort, especially for mainstream or non-tech audiences.
Together, these interfaces reflect the core values of each app: Telegram empowers, WhatsApp protects quietly.
🧭 9. Which One Should You Choose in 2025?
🔸 Choose WhatsApp if:
- You want default end-to-end encryption on all chats without manual settings.
- You mainly talk to friends/family and need smooth cross-platform calling, media, and backup.
- You don’t need anonymity, and trust that Meta won’t abuse metadata.
✅ Ideal for: general users, family chats, small businesses in regulated markets.
🔸 Choose Telegram if:
- You want more control over identity, including username-based chatting.
- You value censorship resistance, flexible privacy settings, and open app code.
- You can remember to manually enable Secret Chats for end-to-end protection.
✅ Ideal for: activists, journalists, users in authoritarian countries, tech-savvy users.
🎯 Bottom Line:
Telegram gives you more visible freedom. WhatsApp gives you stronger invisible encryption.
But neither is perfect:
- Telegram’s E2EE is not default.
- WhatsApp collects extensive metadata.
- Both rely on trust — just in different ways.
As with all security decisions: understand your threat model.
Not everyone needs anonymity. Not everyone can afford trust.
So ask yourself not just “Which app is more secure?”
But rather:
🧠 “What am I protecting, and from whom?”
❓ FAQ
Q1: Can Telegram see my messages?
Yes, unless you’re using Secret Chats. Regular chats are encrypted in transit but stored on Telegram’s servers in decryptable form.
Q2: Can WhatsApp read my messages?
No. All personal chats are end-to-end encrypted by default, even group chats and calls.
Q3: Are my phone number and metadata exposed?
- WhatsApp: Yes, always.
- Telegram: Can be hidden via username — but not fully anonymous.
Q4: Which app is better for political activism?
Telegram — due to its resistance to censorship, anonymous usernames, and global availability (despite bans).
Q5: Is either app audited by independent security researchers?
- WhatsApp: Signal Protocol is peer-reviewed.
- Telegram: MTProto has partial external review, but not fully audited.
📘 Glossary
| Term | Meaning |
|---|---|
| E2EE | End-to-End Encryption – only sender and receiver can read the message |
| Metadata | Data about data – who, when, how long you chatted (but not message content) |
| MTProto | Telegram’s custom encryption protocol |
| Signal Protocol | Open encryption standard used in WhatsApp, Signal |
| Secret Chat | Telegram’s optional E2EE chat mode |
| Zero-Day | A software flaw unknown to developers — exploited before patches |
| Open Source | Code that can be viewed, reviewed, and modified by anyone |
| Proxy (MTProxy) | Special server that hides Telegram traffic to bypass censorship |
| Domain Fronting | Technique to disguise app traffic as innocent HTTPS |
